Coulomb's Law
An introduction to Coulomb's Law
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 02-11-2023
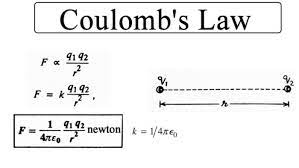
Coulomb's Law is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that describes the electrostatic interaction between charged particles. Named after French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, this law quantifies the force between electric charges and is essential in understanding the behavior of electrically charged objects.
Explanation:
Electric Charge: Coulomb's Law applies to objects with electric charges. These charges can be positive or negative, where like charges repel each other, and opposite charges attract.
Inverse Square Law: Coulomb's Law follows an inverse square relationship. This means that the force is directly proportional to the product of the charges but inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. As charges move farther apart, the force diminishes rapidly.
Direction of Force: The force acts along the line connecting the two charges. It is attractive if the charges have opposite signs and repulsive if they have the same sign.
Superposition Principle: Coulomb's Law can be extended to more than two charges by applying the superposition principle. This principle states that the total force on a charge is the vector sum of the individual forces due to all other charges.
Significance:
Coulomb's Law is of paramount importance in electromagnetism and plays a fundamental role in numerous areas:
Electrostatics: It explains the behavior of static charges and provides insights into phenomena like the attraction of electrons to protons within atoms.
Electric Fields: It serves as the foundation for understanding electric fields. The electric field created by a charge is used to describe how other charges interact with it.
Electrostatic Force: It governs the behavior of electric charges in circuits, electronic devices, and the operation of electric motors, generators, and other electrical equipment.
Nuclear Forces: Coulomb's Law is also related to the forces that act within atomic nuclei, where it competes with the strong nuclear force in determining the stability of atomic nuclei.
In summary, Coulomb's Law is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that quantifies the force between electric charges. It provides a critical framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of charged objects and is central to various aspects of electricity and magnetism.
Cooment List
Leave a Comment.