Lambert's Cosine Law
An introduction to Lambert's Cosine Law
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 02-11-2023
We have studied various concepts of optics in our previous sessions. We have come across various laws like snell’s law, laws of reflection, and many more. In this article, let us learn about Lambert’s cosine law and luminous flux derivation.
Lambert's Cosine Law, also known as the Lambertian reflectance, is a fundamental principle in optics that describes the relationship between the luminous intensity of light, the angle of incidence, and the amount of light reflected off a surface. It is particularly important when dealing with diffuse reflection, where light scatters uniformly in all directions.
Explanation:
Luminous Intensity (I): Lambert's Cosine Law focuses on the luminous intensity, which is the amount of light emitted, reflected, or passing through a surface. Luminous intensity is often measured in candelas (cd).
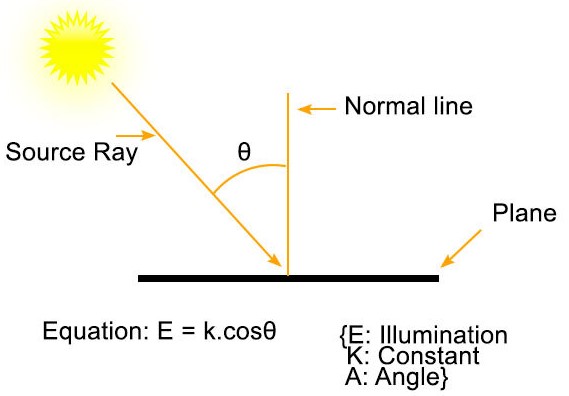
Angle of Incidence (θ): Lambert's Cosine Law states that the luminous intensity of light reflected off a surface is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle of incidence (θ). The angle of incidence is the angle between the incoming light and the normal (perpendicular line) to the surface.
Diffuse Reflection: This law applies primarily to Lambertian surfaces, which exhibit diffuse reflection. Diffuse reflection occurs when light hits a rough or irregular surface, causing it to scatter uniformly in all directions.
Mathematical Representation:
Properties and Significance:
Uniform Scattering: Lambert's Cosine Law is particularly useful for modeling surfaces with uniform scattering properties. It's commonly used in computer graphics, computer vision, and photometry to simulate the reflection of light from matte or non-glossy surfaces.
Inverse Square Law: It's important to note that Lambert's Cosine Law is an idealization and simplification. In reality, light intensity can vary due to factors such as surface properties, surface roughness, and the behavior of light at very acute angles. Nonetheless, for many practical applications, it provides a useful approximation.
Applications: Lambert's Cosine Law is applied in various fields, including computer graphics for rendering realistic materials, photometry for analyzing light levels and brightness, and remote sensing to understand how light interacts with surfaces on the Earth's surface.
In summary, Lambert's Cosine Law is a fundamental concept in optics that relates the luminous intensity of reflected light to the angle of incidence, especially for surfaces with diffuse or Lambertian reflectance characteristics. It has practical applications in a range of fields where understanding light reflection and scattering is essential.
Lambert’s Cosine Law Explanation
Lambert’s cosine law states that the radiant intensity from the ideal diffusely reflecting surface and cosine of the angle θ between the direction of incident light and surface normal are directly proportional. This law is named after Johann Heinrich Lambert which is studied in optics and is also known as Lambert’s emission law or cosine emission law.
Diffuse Reflection
Diffuse reflection can be defined as the type of reflection of light or an incident ray where scattering happens at many angles and not just at one angle. Lambertian reflectance is the property exhibited by diffusely reflecting surface.
Lambertian reflectance is defined as that property of substances due to which they appear equally bright when from any angle.
This is the main difference between specular reflection and diffuse reflection.
Examples of Diffuse Reflection
Paints: The matte paints that are used in home painting exhibit diffuse reflection while the glossy paints reflect diffusely along with specular reflection.
- Frosted glass bulb
- Human eye: The primary mechanism of the human eye is to reflect the incident ray in angles which is based on diffuse reflection.
Luminous Flux Derivation
Luminous flux is also known as luminous power which is the measure of the power of light perceived.
Luminous flux derivation is as follows
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q1
State Lambert’s cosine law
Lambert’s cosine law states that the radiant intensity from the ideal diffusely reflecting surface and cosine of the angle θ between the direction of incident light and surface normal are directly proportional.
Q2
What is Lambert’s cosine law also known as?
Lambert’s cosine law is also known as Lambert’s emission law or cosine emission law.
Q3
Define Lambertian reflectance.
Lambertian reflectance is defined as that property of substances due to which they appear equally bright when from any angle.
Q4
State true or false: The frosted glass bulb undergoes diffuse reflection.
True.
Q5
What is luminous flux?
Luminous flux is also known as luminous power which is the measure of the power of light perceived.
Cooment List
Leave a Comment.